Last Updated on April 25, 2023 by Rod Olivares

A whole house generator, or standby generator, is a versatile and powerful machine that can be used to power up your entire home when the grid goes down.
What differentiates it from a portable generator is that it comes with an automatic transfer switch (ATS) – which enables your home’s breaker panel to automatically switch to the generator power source during a power outage.
Generators come in all different shapes and sizes. From small, portable generators that can power a few small appliances, to large, standby generators that can power your whole home – or even the whole neighborhood!
How Much is a Whole House Generator Unit?
Costs vary widely depending on wattage, but typically range from $4,000 to $12,000 for the average residential unit. The most expensive generators are industrial-sized units which could cost upwards of $30,000 or more in some cases.
What size generator do you need to power your whole house? That largely depends on what appliances you want to power in the event of a power outage.
Make a list of all the appliances in your home and calculate the total amount of running (or rated) wattage and the total amount of starting (or peak/surge) wattage you need to determine what size generator you require. Here’s a handy generator size calculator to help you do that.
Once you know how much wattage (running/starting) is required to power your whole home, you may choose whether to get a whole house generator or a partial house generator.
In some cases, you might want to settle for a partial house generator to lower the overall cost. If you only want to power essential appliances such as your refrigerator, a few lights, and a gas heater or air conditioner this would be enough.
How Much Does It Cost to Install a Whole House Generator?
Now that you have an idea of what size generator you need, let’s talk about how much it costs to install one in your home.
In general, the cost of installation depends on the size of your generator, where you’re going to install it, and your electrician’s hourly rate. That’s why it’s so important to know what you need first before shopping for your unit.
Installation costs can vary depending on its placement in relation to your home’s breaker panel(s) and gas/electric meters.
If your unit is installed on one side of the house and your gas/electric meter is on the other side, then you can expect costs to be a little higher than average.
Installing a generator in your home will usually cost as much as what you paid for your unit. So if your generator unit costs $5,000, expect to pay close to $5,000 to install it in your home. This isn’t always true because other factors may come into play, but it’s a good rule of thumb when planning your budget.
Of course it’s always a good idea to talk to an industry specialist to get a more accurate estimate. In some cases, you might need certain electrical upgrades or repairs in order to install your generator adding to the overall cost.
How Much Does It Cost to Maintain a Whole House Generator?
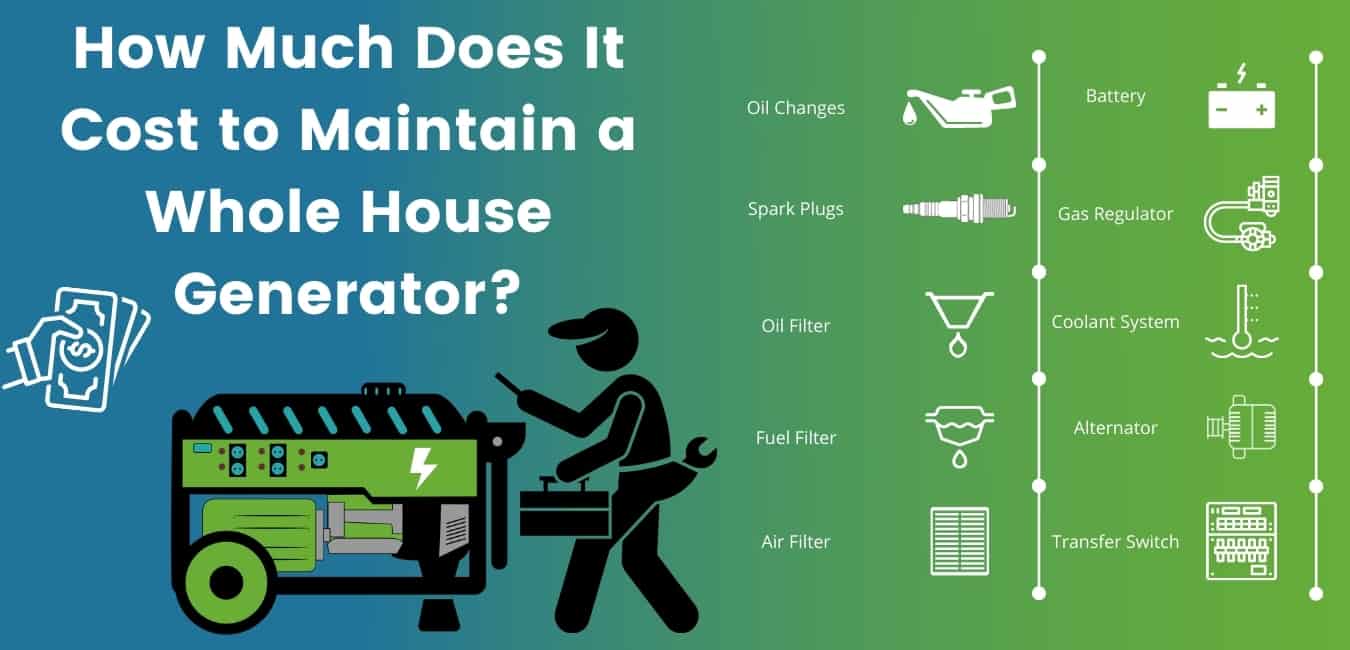
Although the bulk of the cost of a whole house generator is the installation and the cost of the unit itself, it’s important to account for the generator cost of maintenance too.
It’s a good idea to schedule maintenance for your whole house generator every 6 to 12 months.
The most important part of generator maintenance is to change the oil and filters every year, but there are other tasks that need to be completed too. Work out a maintenance schedule with a qualified technician.
The technician can perform a more thorough inspection to ensure that your generator keeps running smoothly, and to prevent any accidents or potential disasters from happening. Expect to pay around $65 to $85 per hour, depending on the technician’s rate.
During maintenance, a technician will inspect and maintain the following:
Oil Changes
Oil in a standby generator is responsible for maintaining its mechanical components and safeguarding them against wear. It keeps all moving parts well-lubricated, preventing any damage that may be caused by friction or heat during operation. That’s why regular oil changes are critical to ensure that your generator continues to run smoothly.
Damage or corrosion can also occur over time if there is a lack of protection from dust or other dirt particles that can enter through open vents. Regular oil changes prevent this from happening.
Spark Plugs
Spark plugs are a small yet essential part of your standby generator. It’s responsible for emitting a small electric charge that helps generate the power needed to start up an engine. That’s why they must be inspected regularly and replaced if needed.
Spark plugs are responsible for igniting gas during combustion cycles by sending out an electrical current between electrodes – which can be obscured if dirt and other debris builds up inside the engine over time.
This disruption could lead directly to malfunctions like freezing, stalling, or even triggering fires due to their proximity to combustible gasses. If a spark plug is damaged, it will also prevent your generator from starting properly.
Oil Filter
Oil filters are responsible for keeping the oil in standby generators clean. It filters contaminants that can corrode or damage metal parts and cause malfunction. A cleaner engine means better performance and less wear on parts, leading to lower repair bills over time.
The biggest sign of a faulty or dirty oil filter is an increase in the noise level coming from your generator. This usually means there are contaminants present inside the engine that could be due to a clogged oil filter.
If left untreated for too long, these particles can enter into other parts such as bearings and gears potentially causing permanent damage over time requiring costly repairs.
Fuel Filter
The fuel filter cleans the fuel by trapping dust, debris, and other particles as it goes through. It prevents these contaminants from reaching your generator’s inner components and ensures optimal performance.
If you don’t have your fuel filter changed or cleaned out regularly, dirt and debris will accumulate on its surface. This buildup can result in inefficient combustion, lowering engine performance and increasing dangerous CO gas emissions.
In order for the fuel filter in a standby generator to function properly, it should be replaced yearly or as directed by manufacturer instructions.
Air Filter
Similar to the oil and fuel filter, the air filter keeps dust, mold, pollen, and other debris from clogging up internal components. It cleans the air before it gets mixed with the fuel during ignition to start up the engine.
Maintaining the air filter in a standby generator is important because it prevents debris from entering into your engine and damaging other components.
A dirty air filter can reduce the overall performance of your standby generator. A blocked airflow will decrease efficiency and lead to damage of parts, resulting in expensive repairs.
Battery
A battery stores electricity to power the standby generator’s motor. It acts as an ignition switch. Without it, you wouldn’t be able to start your engine and power up your house when there’s an outage.
Over time, batteries will naturally lose their capacity to hold a charge. This process is unavoidable. Manufacturers generally advise replacing the battery after 2-3 years.
If the battery is not replaced in time and loses its charge-holding capacity, your generator will not be able to start up during an emergency.
Gas Regulator
The gas regulator is responsible for ensuring there are no fluctuations in gas pressure, which can lead to damage or poor quality output in your standby generator.
It controls the flow of fuel by keeping the gas pressure consistent in order to supply the right amount of fuel for operation. A faulty or broken regulator will result in excess or insufficient amounts of fuel or pressure and will reduce your generator’s performance over time.
Coolant System
The generator’s coolant system keeps the standby generator at an optimal operating temperature by circulating air or cooling liquid around its internal components.
A damaged coolant system will increase the risk of overheating. That kind of damage could affect the entire engine and result in costly repairs, or worse, you might even have to replace your entire unit.
Alternator
The alternator is responsible for producing electricity in a standby generator. It takes the mechanical energy created by the generator and converts it into electrical energy – or what we know as an alternating current (AC).
The alternator is an essential part of your standby generator. Without it, the unit won’t be able to generate electricity!
For maintenance, it must be kept clean and free of debris and should be inspected regularly to ensure there aren’t any corrosion, loose parts, or excess vibration that may indicate a problem.
Transfer Switch
The transfer switch is responsible for switching your home’s electrical system from utility power to the backup source of electricity produced by your standby generator during a power outage. It does this safely and automatically.
Maintaining the transfer switch is important to ensure it can effectively power essential appliances during an outage and prevent failure that can cause serious damage to both people and property.
If it malfunctions, it could cause an unexpected power surge into your home that could cause accidents.
Repairs
Repairs range from $75 to $300 for minor repairs and replacement of parts, and up to $2,000 for major repairs.
To avoid expensive repairs and to ensure a long lifespan for your generator, it’s important to have it inspected and maintained once or twice a year. A well-maintained unit can last up to 20 years.
We also recommend running your generator for 15 minutes every other week to maintain its various parts and ensure everything is in working order. This will usually cost no more than $100 per year in terms of fuel.
How Much Does Each Fuel Type Cost for a Whole House Generator?
The cost of running a whole house generator largely depends on the size of your generator (rated wattage), how much power you’re consuming (electrical load), and the local cost of the fuel source, such as natural gas or propane. Whole house generators use one (or two) of these types of fuel:
- Natural gas. This is the most popular fuel option for whole house generators because it’s inexpensive, burns cleanly and efficiently, and provides continuous supply. The major drawback of natural gas as a generator power source is that your home must already have access to a natural gas line. Otherwise, you will have to rely on stored fuel.
- Propane. The most common stored fuel source for generators. Its long shelf life means you won’t have to worry about the potency of your generator fuel supply diminishing over time, making it a popular choice for whole house generators.
- Diesel. This fuel doesn’t age as quickly from mechanical stress compared to gasoline because it uses compression heating rather than spark ignition. It’s also safer than gasoline and natural gas because it is non-combustible.
- Gasoline. For a whole house generator, gasoline is the least ideal option. They’re best suited for portable generators and as an alternative fuel source for dual fuel generators. Their main advantage is that they are easily available.
It’s important to remember that fuel cost largely depends on your location and how much power your house consumes per hour of operation.
You also need to consider the fuel consumption rate of your individual unit. It varies depending on size, make, and model so be sure to check the user manual.
In general, 1kW equals 1.34102 HP (Horsepower), which consumes approximately 10,000 BTU (British Thermal Unit).
Here’s a comparison table estimating the cost of running a whole house generator per hour at full load:
| Generator Size | |||
| Fuel Type | 10kW
13.41 HP |
20kW
26.82 HP |
30kW
40.23 HP |
| Natural Gas
1 cubic foot = $0.018 |
129.32 cu ft /hr
$2.33 /hr |
258.63 cu ft /hr
$4.66 /hr |
387.95 cu ft /hr
$6.98 /hr |
| Propane
1 gallon = $2.30 |
1.47 gal /hr
$3.38 /hr |
2.93 gal /hr
$6.74 /hr |
4.40 gal /hr
$10.12 /hr |
| Diesel
1 gallon = $3.34 |
1.04 gal /hr
$3.47 /hr |
2.07 gal /hr
$6.91 /hr |
3.11 gal /hr
$10.39 /hr |
| Gasoline
1 gallon = $3.14 |
1.18 gal /hr
$3.71 /hr |
2.35 gal /hr
$7.38 /hr |
3.53 gal /hr
$11.08 /hr |
How Much Does It Cost to Install and Maintain a Natural Gas Line?
A natural gas pipeline is an underground pipe system that transports natural gas from your local utility company to the gas line in your home.
Although some may already have a gas line installed, not every property comes with the necessary infrastructure for natural gas distribution. In some cases, you might have to install gas piping yourself.
Check with your local utility company to determine whether or not natural gas piping is available for your property.
Natural Gas Line Installation Costs
If you’ve ensured that natural gas distribution is available in your area, you might consider installing a natural gas line to your home.
The gas line will run from your home’s meter to your standby generator or any gas-powered appliance. Then, your home’s meter will be connected via service line to the street, where the main natural gas distribution line should be.
Gas lines can be expensive, costing homeowners between $500 and $2,000 on average.
The cost varies depending on factors such as diameter, material, and length, as well as which appliances you wish to connect to the line.
In some cases, you might even have to install a gas meter if your home doesn’t have one, which could add to the total cost.
If you already have an existing line, expect to pay around $200 for a 10-foot gas line extension. However, if your service line requires several hundred feet to reach your home plus a 25-foot interior gas line, prices can reach up to $5,000.
Several factors influence the price of your gas line installation. The material used and the cost are affected by whether the line is inside or outside your home.
Installing lines in difficult-to-reach areas, as well as digging or trenching, increases the cost of installation.
Extending existing gas lines will cost less than installing a new one because gas plumbers usually install these lines.
Call your utility company to get the proper clearances. In most cases, you’ll also require a permit before installation from your town or city hall.
Talk to a plumbing specialist to determine how much your installation will cost. Hourly rates can vary from $45 to $200 per hour depending on the contractor and your location, so have a list of options before you begin the project.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Having natural gas already available in your home is ideal during emergencies because you don’t have to worry about running out of fuel or exchanging empty gas fluid cylinders.
Gas lines are often installed underground, making them less likely to be disrupted during natural disasters. Not only that, it’s also the cheapest among all the fuels.
The problems with natural gas lines are that they require strict maintenance and regular inspection for leaks. Pipes tend to degrade over time and could lead to hazardous situations if not properly maintained.
Natural Gas Line Maintenance Costs
To prevent accidents from happening, your gas line has to be inspected at least once a year. Expect to pay around $50 to $75 to have it properly inspected.
If your gas line is showing signs of corrosion, it’s important to have it repaired as soon as possible.
Depending on location and size, this will cost anywhere between $16 to $35 per linear foot to replace damaged pipes.
Wrapping up
While they may be expensive, standby generators can be well worth the price. It offers comfort, safety, and convenience during emergencies and whenever the electrical grid goes down.
In summary, purchasing a standby generator for your home will cost anywhere between $4,000 to $12,000 for an average residential unit, depending on your power needs. Still, it may cost more if you have a larger house.
Installation costs are usually comparable to the cost of your unit, so if it costs $5,000 then you can expect to pay around the same amount for installation.
However, this is not always the case. Other factors will also determine the cost such as the contractor’s hourly rate and the placement of your generator.
That said, we can say the total estimated upfront cost for installing a whole house (or partial house) generator ranges from $8,000 to $24,000 on average for a small to medium-sized house.
Annual maintenance and repair costs will vary depending on your unit, but they will likely range from $165 to $800. Major repairs might cost up to $2,000 so it’s important to check your generator once or twice a year.
These costs are just estimates. Actual prices will depend on your location and local contractor rates. But hopefully this article has given you a good place to start planning your budget!
If you don’t mind manually starting up a generator during a power outage and only want to power a few key appliances, you might want to consider buying a portable generator instead. They cost much less and there’s no need for installation, so they’re perfect if you have a limited budget but want to be prepared for emergencies!

Scott Krager purchased generatorgrid.com in the summer of 2020 and quickly began to buy every generator under the sun! He currently has over a dozen generators and the number is growing quickly. He lives in Portland, OR near his family and friends.
GeneratorGrid.com is an independent review business. I am not affiliated with any manufacturers and do not accept paid reviews. When you buy through my links, I may earn a commission which helps me purchase more generators for testing. - Scott Krager


I have a farmhouse in the countryside, and I face load shedding issues there. So, based on what I have learnt from your article, I was looking to purchase a whole home generator that can run on natural gas or propane. And now that I’ve learned everything there is to know about it, I’m even more inclined to purchase one. Thank you for sharing this useful information!
Happy to hear we helped you!